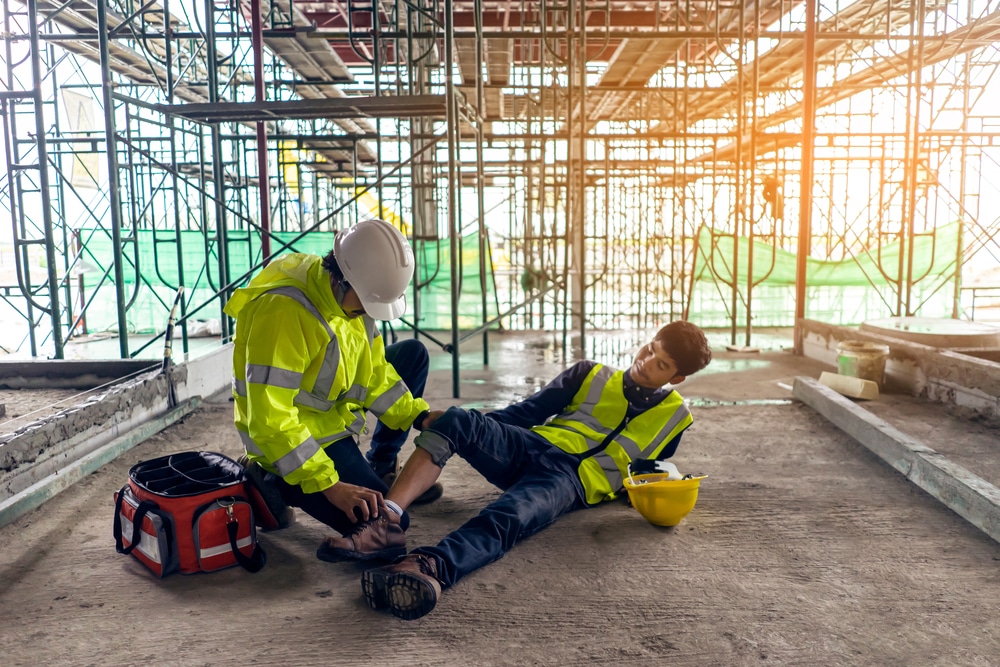
Work-related injuries are common and inevitable whether you are a blue- or white-collar team member. Standing for an extended period, tripping off the stairs, or falling off of debris—a foot injury has increased in the labor industry.
Employees dread these situations as it may take them some time off work, loss of wages, incapability to return to body normal function, get laid off, and create emotional and financial distress to them and their families.
The employer must assure that their employees are eligible to claim worker’s compensation insurance. Injuries may be minor, but in severe cases, the proper medical intervention must be given. You may check https://www.tetonfootandankle.com for efficient and successful injury treatment.
Depending on the severity and type of the foot injury, it will considerably impact the life and career of a team member. Here are two options for treatment and recovery.
1. Conservative Medical Strategies
Conservative medical strategies are the non-surgical and non-invasive interventions used to treat injuries. Using these methods may permit the team member to continue working while being treated. They cost less and prevent the individual from being put on bed rest or admitted to the hospital.
Many acute, chronic, and recurring conditions and injuries are successfully treated conservatively. Moreover, it lessens the pain and probable complications, unlike going through invasive ones.
Conservative medical strategies include the following methods:
-
RICE Method
Rest, Ice application, Compression, Elevation, or the RICE method is the most basic conservative intervention. This must be done right after the injury to modulate the swelling, pain, and inflammation.
In mild cases of a foot injury, such as ankle sprain or bruising due to bumps or foot hit by a heavy object, RICE is highly recommended as the primary intervention.
-
Oral Medication
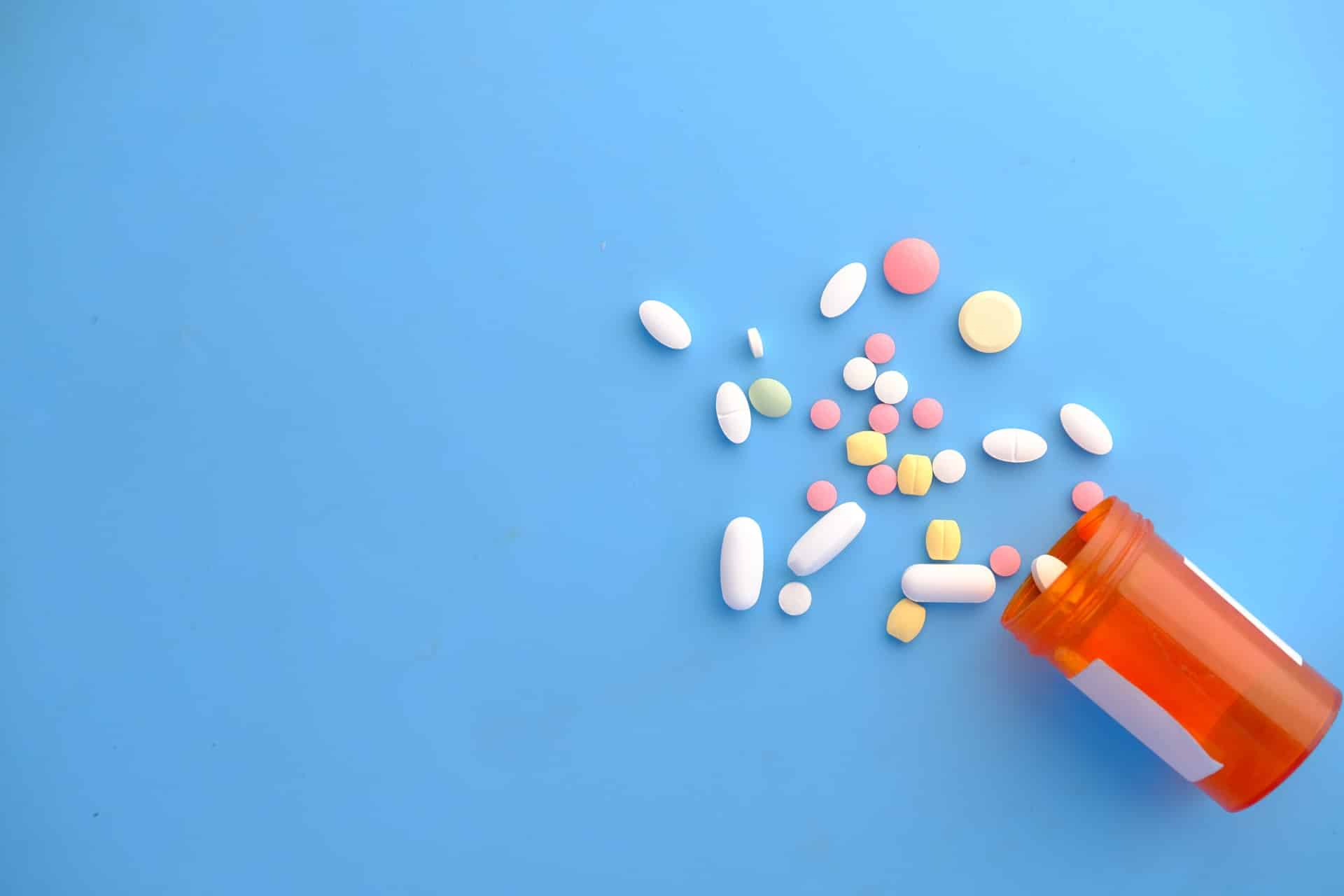

Physicians highly recommend using Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and high temperatures. It is commonly used in headaches, sprains, strains, arthritic pain, and other chronic conditions.
The presence of pain may negatively affect the team member to force him to miss work. Employees who suffer from an ankle sprain, plantar fasciitis, ingrown toenails, arthritis, and Morton’s neuroma can benefit from the use of NSAIDs.
The team member is then allowed to continue working while under treatment and recovery. Pain is minimized and controlled, though the patient may be advised to avoid heavy lifting, distant walking, and strenuous activities.
-
Topical Analgesic
Topical analgesics may be in the form of a spray, cream, gel, lotion, or patch. They offer temporary pain relief when applied to the skin over painful muscles or joints that lasts for a few hours.
The following are common types of topical analgesics that are generally used:
- Prescription NSAIDs – These are a topical form of oral NSAIDs; they can only be bought with a prescription from a doctor or qualified nurse practitioner.
- Lidocaine – This may come in patch or gel form. However, a medical clearance from a doctor is needed due to its adverse effects.
- Counterirritants – Camphor, menthol, capsaicin, and methyl salicylates are examples of counterirritants. They differ in composition but give the same cooling or burning effect to mask the pain.
Team members will be able to work by constantly applying the topical analgesics when they wear off. These may also be used if you experience ankle sprains, arthritis, tendonitis, and plantar fasciitis.
-
Hot Packs/Cold Packs
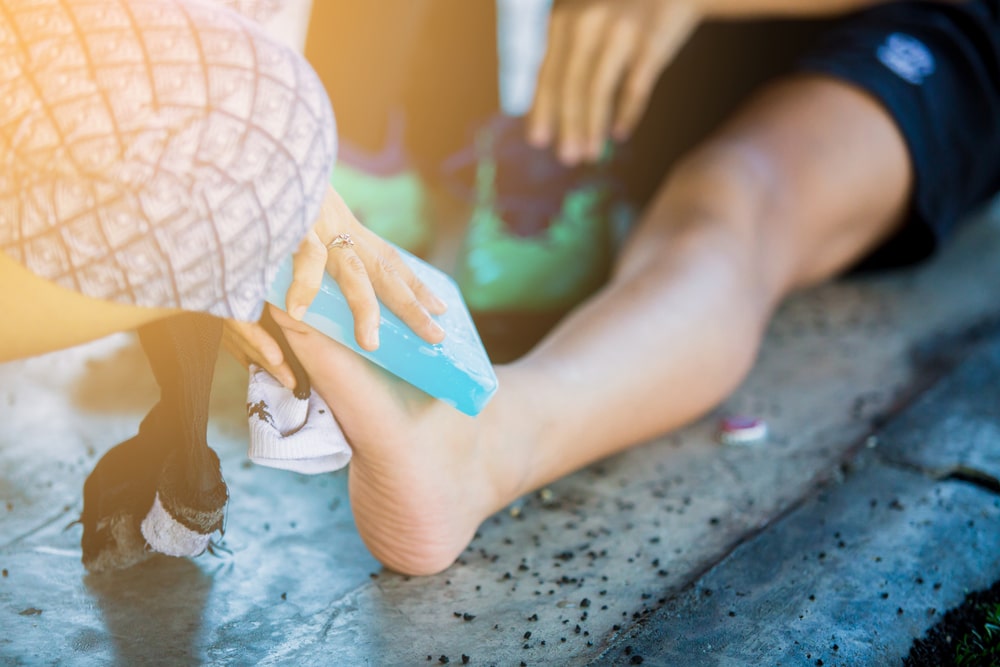

- Cold packs are used for acute Grade 1 and 2 ankle sprains or muscle strains. Within 48 hours, it should be applied intermittently for ten minutes. Team members must be aware of the series of effects—from intense pain, burning sensation, aching pain until it becomes numb. Cold packs help in reducing the swelling, inflammation, and pain of the injured area.
- Hot packs are used for chronic ankle and foot conditions, such as plantar fasciitis and arthritis. They distend the blood vessels to increase blood flow, relax muscles, and relieve the affected joint or muscle pain.
-
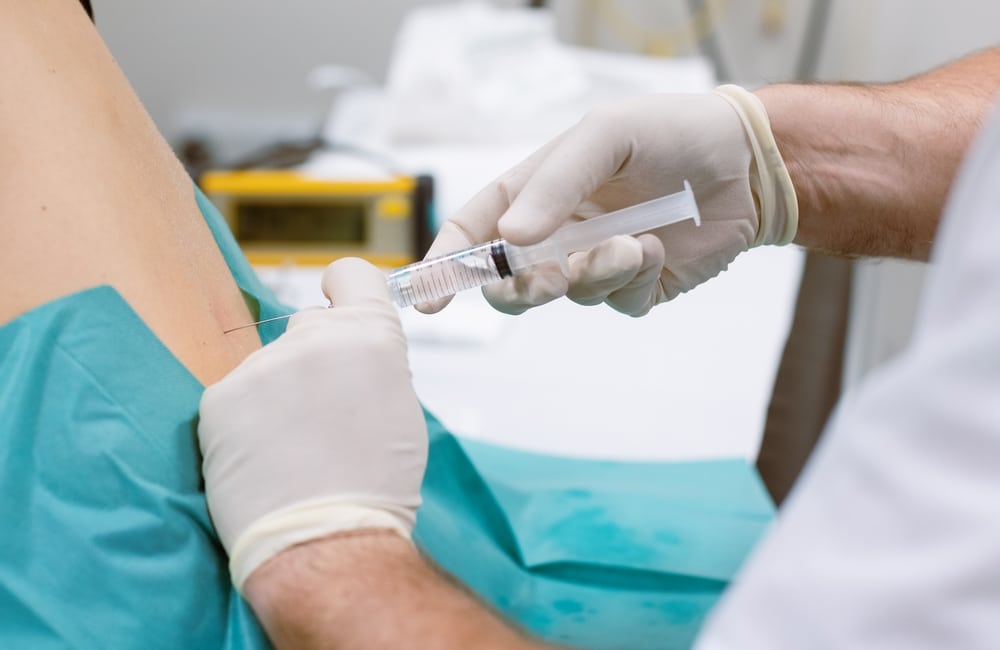
Cortisone Injections
Cortisone injections are administered to painful joints. Moreover, this has positive benefits that may last two to six months; hence it may be a good choice for treatment. They are costly, and optimal effects are seen after two weeks.
-
Plate-Rich Plasma (PRP) Injections
PRP is the liquid component of the blood that delivers the body’s hormones, nutrients, and protein. The foot is the most posterior part of the extremity. Hence, there is a scarcity of nutrients and blood supply in the injured area during inflammation.
In PRP, the individual’s plasma is extracted and administered to the affected area to facilitate healing. It is costly, and only a handful of clinics and hospitals perform this procedure. In addition, PRP injections last about six to nine months. Thus, they may be a good option for chronic pains acquired from a work injury.
-
Physical Therapy (PT)
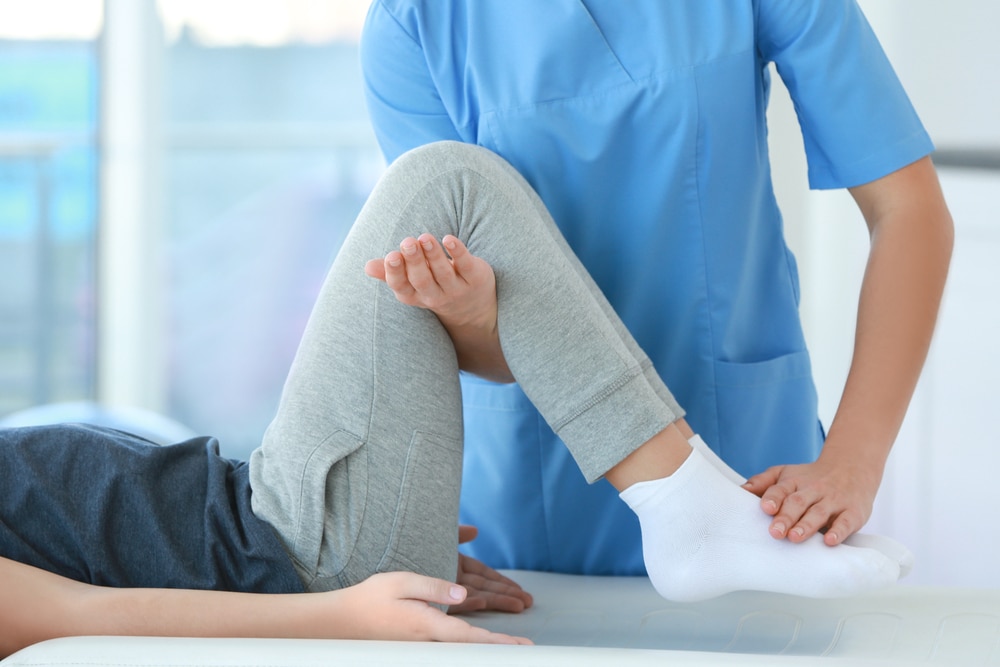

Physical therapy provides a variety of conservative approaches to deal with work-related injuries. A team member may attend three to four sessions in a week and are scheduled after work. Thus, work schedules won’t be interrupted.
Here are the conservative approaches that a PT provides:
- Range of Motion Exercises
Range of motion (ROM) examines the extent of movement a joint or extremity is capable of. Work-related foot injuries may be acute or chronic; thus, they may have resulted in restrictive motions due to pain, swelling, or stiffness. Complete ROM of joints and muscles is essential for effective functional movements at work.
Depending on the severity and type of injury, therapists may perform Passive, Active, and Active-assistive ROM exercises during the session. Pain, swelling, or stiffness may lead to immobility of the foot. Team members may walk in antalgic gait or with postural deviations to avoid pain.
ROM exercises re-educate the muscle and joints of the proper way to use the affected area. It also prevents muscle atrophy, increases endurance and strength, and assists in blood circulation to relax the muscle and decrease pain.
The physical therapist ensures that the team member can get back to work with proper knowledge of using the affected injury without triggering tension and pain and preventive ways to avoid recurrence of injuries such as ankle sprain or strain.
- Stretching Exercises
Pain, swelling, and stiffness may lead to hypomobility, which may result in structural deformities. In addition, it may cause the soft tissues to lose their extensibility, weakness, and shortening of opposing tissues. However, this is preventable.
After a healed fracture, ankle sprain, or strain, stretching exercises are beneficial to elongate the muscle and improve blood circulation to improve muscle function.
There are various types of stretching, such as static, cyclic/intermittent, manual, mechanical, passive, active, or self-stretching. A physical therapist will determine the appropriate intensity, duration, speed, frequency, and mode of stretch to ensure that the team member can perform his regular job efficiently when he is back at work.
- Peripheral Joint Mobilization (PJM)
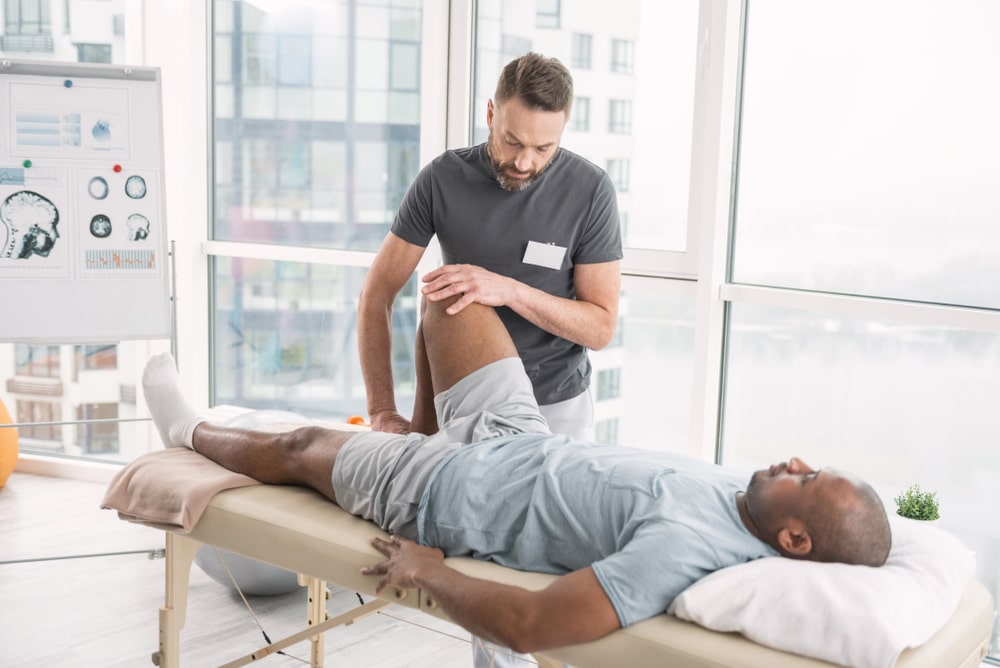

PJM is the manual therapy approach used to regulate pain and joint dysfunctions. The foot comprises 34 joints and 100 muscles. Thus, an ankle sprain, strain, or healed fracture creates stress on joints and muscles weakness.
Pain and muscle guarding may have rendered the joints to become restrictive and hypermobile. Gentle joint-play techniques will help in restoring the mobility and integrity of the joint.
- Aerobic Exercises
When a team member acquires severe work-related injury, he may be put on bed rest for some time. It may result in deconditioning of the injured area or even the whole body. A decrease in maximum oxygen consumption and muscle strength may lead to muscle atrophy, weakness, or affect the individual’s overall health.
Deconditioning may decrease muscle mass, strength, orthostatic tolerance, cardiovascular function, and bone mineral density. When a team member resumes working, it is a must that he is fully fit and injury will not recur.
- Proprioceptive Exercises
Balance, stability, and body coordination are maintained due to the help of the leg gravity muscles and integrity of the 26 bones of the foot, ligaments, and tendons. Due to foot injuries—such as ankle sprain, strain, or fracture—there may be loss of proprioception in the ankle.
Upon the healing and recovery stage, a team member is prone to tripping, slipping, or falling when the receptors in the ankle area are not stimulated. Proprioceptive exercises help in ensuring the safety and prevention of injury recurrence.
- Taping
Taping is a manual technique used as a joint protective mechanism, especially in doing strenuous activities. It helps in soft tissue compression and restricts the movement of the injured joint.
Each tape is applied individually to cater to unusual anatomy regions. Physical therapists have expertise in taping different kinds of injury areas. While it is an acceptable form of support in all sports, taping can also be used for injured people in various labor industries. It is not bulky; thus, it would not hamper team members while doing their usual routine at work.
- Bracing
A brace is worn in the affected foot to prevent unnecessary movements that may worsen or disrupt the healing stage of an injury. You may buy it in medical equipment stores, sports houses, or malls. It is reusable; thus, it is more cost-effective than taping.
Bracing gives a sense of protection to the team member as it compresses the injured area, resulting in pain-free functional movement in the worksite.
- Modalities
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), contrast baths, whirlpools, ultrasound, and short-wave diathermy are the most common modalities used in physical therapy clinics. They utilize electrical, ultrasonic, conductive heating machines to stimulate the muscles, bones, and nerves. Hence, decreasing the swelling, pain, and inflammation and increasing the healing phase.
2. Invasive and Surgical Approaches
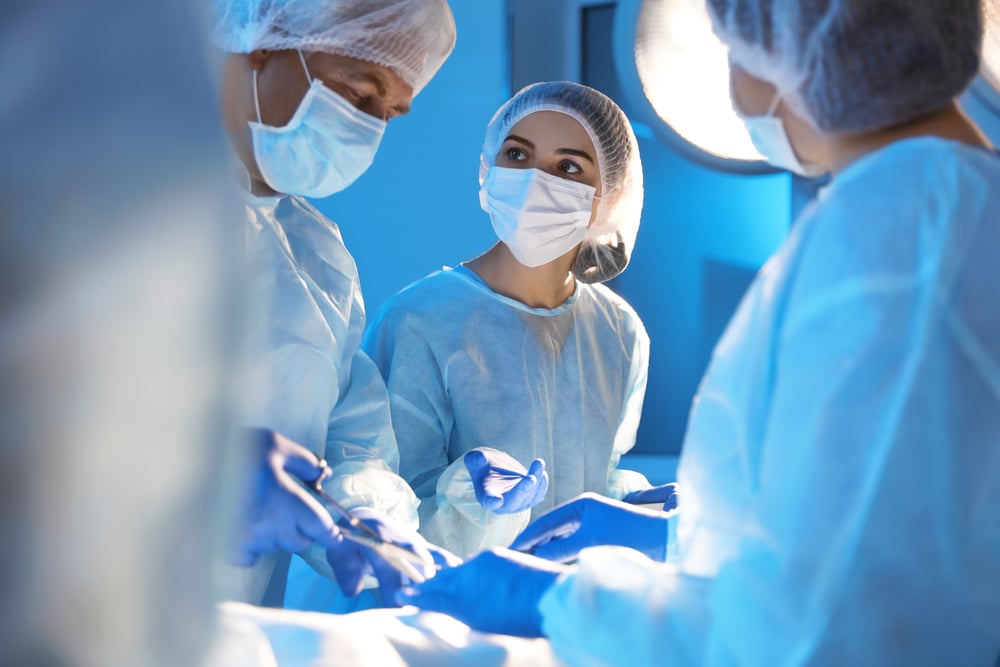
When conservative techniques do not successfully manage a foot injury, invasive and surgical approaches may be the next step. Incapacitating pain, chronic joint swelling, ankle and foot deformation, and marked loss of foot functions may continue to compromise the team member to resume his work significantly.
The impairment’s preoperative examination and functional status are crucial in making effective post-operative management. There are a variety of surgeries performed depending on the type and severity of injury:
- Reconstruction and Decompression
When a heavy object, debris, or machinery falls onto the feet, it may result in considerable damage. This includes the bones, muscles, and nerves. Therefore, reconstructive surgery is needed to repair the damages and salvage the injured extremity.
Some of the procedures are tenoplasty, capsulolabral reconstruction, arthroplasty, ligamentous reconstruction, and chondroplasty.
- Realignment and stabilization
Grade 3 ankle sprain tears the anterior tibiofibular ligament and calcaneofibular ligament completely. It requires either internal bracing surgery or tenodesis of Peroneus Brevis—a muscle in the lower part of the leg.
Other procedures are extensor mechanism realignment, capsulorrhaphy, capsular shift, tendon transfer, or osteotomy.
- Endoscopic Plantar Fasciotomy (EPF)
Prolonged standing at work may result in compression and inflammation of the plantar fascia. Plantar fasciitis manifests as a stabbing pain at the bottom of the foot. EPF has shown effective results, and it is a big help to a team member to resume his work pain-free.
Considered Factors In Planning Treatment For Recovery
The prognosis of foot injuries varies from person to person. Here are the factors that are at play:
- Age
Healing is associated with the immune system’s ability to cope with the changes in the body. Aging affects the production and function of the hormones and cells to heal an injury.
- Presence of Comorbidities
The presence of comorbidities may hamper the healing phase. For instance, in people with diabetes, viscous blood and impaired circulation reduce the number of nutrients, proteins, and hormones delivered to the most posterior part of the body.
- Type and Severity of Injury
Various conservative techniques may treat acute and mild injuries, and a team member may resume work while on treatment. Chronic and severe injuries may need invasive and surgical intervention to alleviate the pain, correct impairments or deformities, and save the foot.
Taking All Into Consideration
Accidents are inevitable, and work-related foot injuries are prevalent. A team member may suffer from pain, functional impairments, emotional stress, economic and non-economic losses. There is a vast array of options for treatment and recovery depending on the severity and type of injury.
Conservative techniques are highly recommended so that a team member may continue to work and earn. However, in irreversible and severe cases, surgeries are necessary. It is essential to consult an experienced doctor to find the best surgical approach. The goal is to help the team member return to his work efficiently. Patient education is crucial to avoid recurrence and to worsen the injury.

